YMCA East Surrey’s Children’s Wellbeing Practitioner (CWP) team provides guided self-help for children and young people experiencing:
Our CWPs are part of YMCA East Surrey’s Emotional Wellbeing and Mental Health service, working across the local community, GP practices, and schools.
Who We Support
We offer support to children and young people aged 4 to 18, using either:
Our Approach
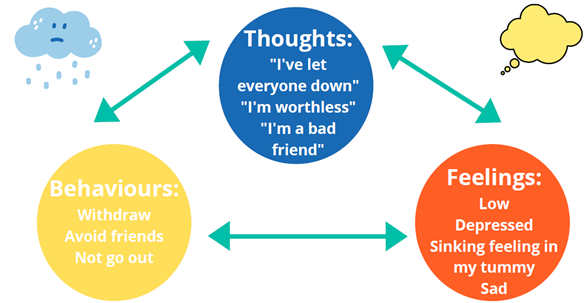
CWPs use Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) principles to help normalise emotions and build healthier patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaviour through structured self-help strategies.
Referrals & Contact
We are currently unable to take any new referrals into our CWP service, please email childrenswellbeingpractice@ymcaeastsurrey.org.uk, if you would like to hear more about other support offers within YMCA East Surrey.
Can refer:
Exclusions (cannot refer):
Cost
Our service is free for all clients.
Confidentiality
We understand how important trust is. Everything shared with us remains confidential and will not be passed on outside YMCA East Surrey or our NHS partners without your consent, unless we believe you or someone else is at risk. In such cases, we will always try to discuss it with you first.